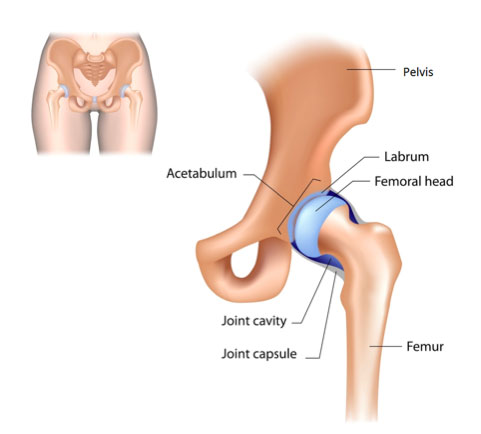
The Acetabulum the femoral head and the ligamentum teres all contribute to the stability of the hip joint. These structures ensure stability of hip joint by preventing hyperextension of the knee.
The Dancer S Hip Anatomy And How The Hip Functions Optimally For The Dancer Kinetica Physiotherapy Balgowlah St Leonards Sydney Australia
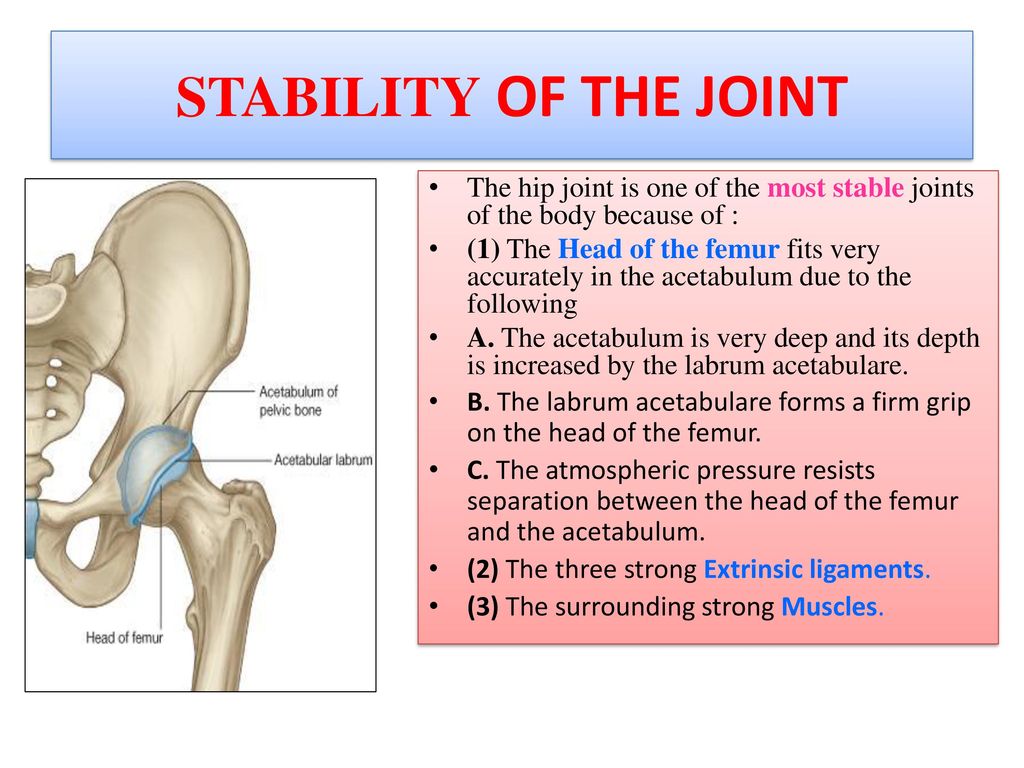
The hip joint is extremely strong due to its reinforcement by strong ligaments and musculature providing a relatively stable joint.
. The shoulder joint is built for mobility. Pages 13 Ratings 100 3 3 out of 3 people found this document helpful. It is deep and encompasses nearly all of the head of the femur.
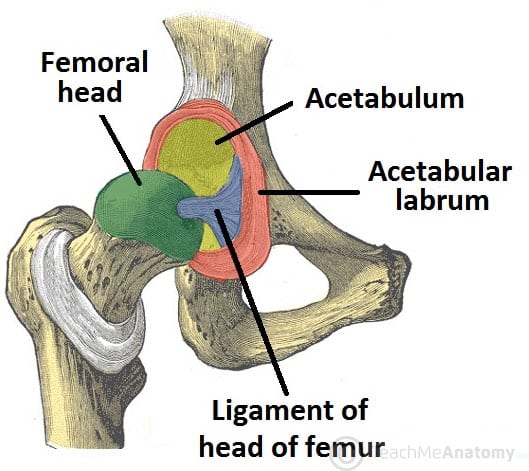
This structure contributes to stability of the hip joint Acetabular labrum. A review of the structure of the hip joint as related to its stability is presented. This structure contributes to stability of the hip.
It contains mechanoreceptors that monitor vibration and tensile loading in the hip joint. Menisci and intracapsular cruciate ligaments. The stability of the hip is increased by the strong ligaments that encircle the hip the iliofemoral pubofemoral and ischiofemoral ligaments.
A ball fitted into a socket. This structure contributes to stability of the hip joint. LeVeau PhD The Hip Joint.
School Mesa Community College. These ligaments completely encompass the hip joint and form the joint capsule. Surrounding the bone are a capsule and tough ligaments which connect bone to bone at the joints.
The pelvis is made up. The osseous anatomy of the femoroacetabular articulation contributes to the hips inherent stability. The hip joint capsule has two layers.
The hip joint is formed by an articulation between the pelvic acetabulum and the head of. A review of the structure of the hip joint as related to its stability is presented. However whilst the hip is more stable the shoulder has a greater range of movement.
In contrast the acetabulum of the pelvis fully encompasses the femoral head and this makes the hip-joint far more stable. Structure Stability and Stress. Singleton PhD Barney F.
It plays a role in normal joint development and in distribution of forces around the joint 9 10. It plays a significant role in the stability of the hip joint as it almost entirely encompasses the head of the femur. Clinical considerations of selected hip abnormalities include a review of changes in normal mechanical.
The hip joint is a spheroidal or ball-and-socket-type synovial joint stabilized by bony and ligamentous restraints. The cruciate ligaments are the structures that are contribute to stability of the hip joint. It has also been suggested it plays a role in compartment of the hip thus helping exert a negative pressure effect within the hip joint 11.
This decreases the probability of the head slipping out of the acetabulum dislocation. A Review Physical Therapy Volume 55 Issue 9 September 1975 Pages 957973. The first structure is the acetabulum.
The fibrous joint capsule is a supporting structure of the hip joint contributing to the joints overall stability. First there is the joint shape. Course Title BIO 201.
There are a number of factors that act to increase stability of the joint. The forces exerted at the hip and along the proximal end of the f. The primary function of the hip joint is to weight-bear.
Unlike the weak articular capsule of the shoulder the hip joint capsule is a substantial contributor to joint stability. What are the two factors that contribute to the stability of the hip joint. The acetabulum bears a prominent semilunar region known as the lunate surface that is covered by articular cartilage.
What factors contributes to stability of. Finally there are the dynamic stabilizers of the jointyour muscles. Each joint has this trade-off that is particular to its function.
The ball-and-socket hip joint is braced by strong muscles and the retinacular fibers of the articular capsule itself. The tiny ligament of head of femur or ligamentum teres does attach to the femur but it isnt strong enough to provide. The zona orbicularis resists joint distraction during neutral positions and its aperture mechanism stabilizes the hip from adverse edge-loading during extreme hip flexion-extension.
Rotator cuff muscles B. Interphalangeal joints joints between talus and tibiafibula NAME TWO IMPORTANT FACTORS THAT CONTRIBUTE TO THE STABILITY OF THE HIP JOINT. Further both anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments ensure tibia does not slide out in front of femur as well as ensuring rotational stability of the knee.
DEEP SOCKET AND LIGAMENTS Name two important factors that contribute to the stability of the knee. Its also strengthened by the iliofemoral ischiofemoral and pubofemoral ligaments inside the capsule. The hip joint is a type of synovial multi-axial ball-and-socket joint.
Hip joint capsular ligaments iliofemoral ischiofemoral and pubofemoral play a predominant role in functional mobility and joint stability. The capsule is thicker anterosuperiorly where the predominant stresses of. To better understand lets look at what determines mobility and stability in your hip joints.
The Acetabulum the femoral head and the ligamentum teres all contribute to. A contribution to joint stability than the glenoid labrum in the shoulder it does serve its purpose. The iliofemoral ligament is considered by most experts to be the strongest ligament in the body.
The forces exerted at the hip and along the proximal end of the femur are discussed in relation to the anatomical position of bone and to normal stresses incurred during standing and gait.

Pdf Can Local Muscles Augment Stability In The Hip A Narrative Literature Review
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy

Hip And Thigh General Introduction Anatomy Hip Joint Ball And Socket Ball Femoral Head Socket Formed By The Three Pelvic Bones Socket Called The Ppt Download
0 Comments